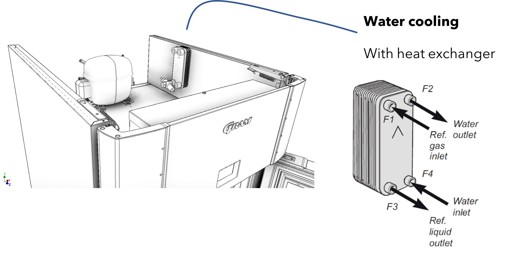
The conventional system – Air cooled
The refrigeration system in a conventional refrigerators and freezers typically uses fan that facilitates the transfer of the heat energy from the condenser to the ambient air. It is a traditional and secure way of cooling the components.
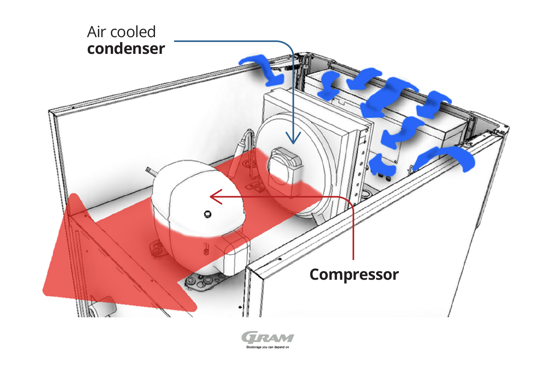
Figure 1 shows a traditional refrigeration system, where ambient air cools the condenser and compressor. The heated air flows into the surroundings.
The ambient air is channelled through the system (see figure 1), moving the heat away and transferring the heat out and into the surroundings. This solution is a simple, flexible, and self-containing plug-and-play system, which can be put into operation and moved at a moment’s notice.
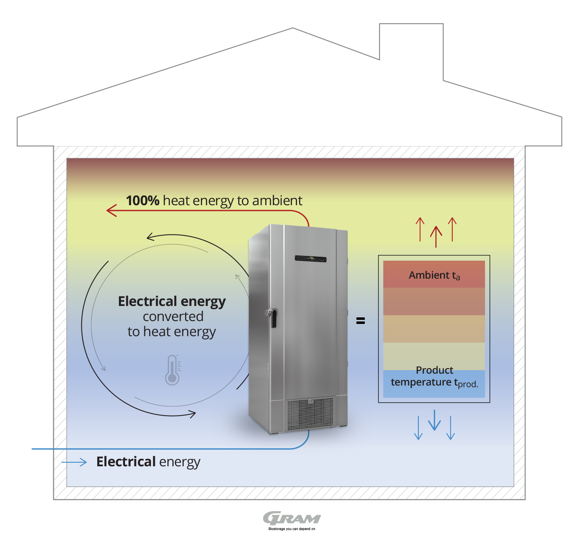
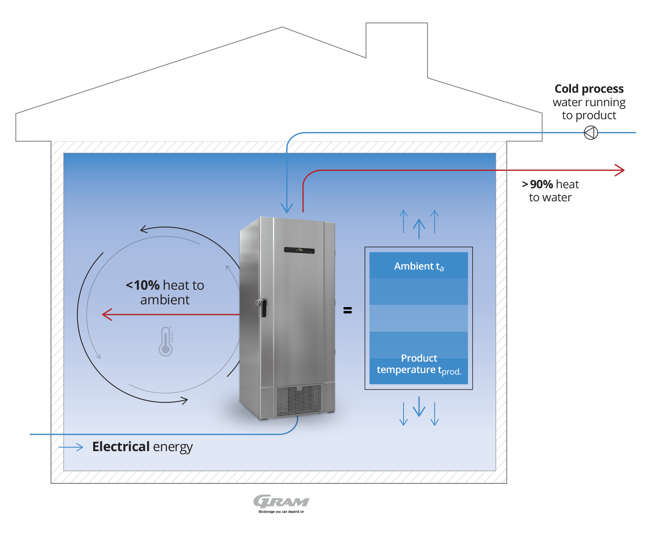
Figure 2: Traditional cooling principle.
This theoretical drawing shows the principle of traditional cooling; Electrical energy is supplied to the cabinet to energise the refrigeration system. The refrigeration system converts electrical energy into mechanical energy inside the compressor, transferring energy between the inside of the refrigerator or freezer and the ambient air, thereby cooling inside and expelling heat to ambient. Since heat is the main bi-product of operation, a refrigerator or freezer will have effect on the temperature in the room.
The illustration above is a stand-alone example, as other factors like; room size, doors, windows, sunlight, ventilation system, other electrical appliances etc., also affect the ambient conditions.